JETRO Invest Japan Report 2021
Chapter2. Japan's Business Environment and Foreign-Affiliated Companies Section2. Improving the Business Environment in Japan
Initiatives for Innovation Cities
Formation of hub cities for international startup ecosystems
Japan faces various social issues such as low birthrate, an aging population, and regional disparities. It is essential to build an innovation ecosystem by incorporating innovative technologies and know-how through open innovation and attracting excellent human resources and funds from overseas to achieve sustainable economic growth. The “Strategy for Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in Japan” also assets that the establishing an innovation ecosystem is one of the pillars for achieving the policy goals mentioned in Chapter 2 (1) above. Specifically, the strategy states to create international innovation ecosystem cities that are internationally open, centered around the top universities in the region, and promote the accumulation of foreign startups, overseas human resources (teachers, researchers, entrepreneurs, etc.), and investors in a unified and integrated manner.
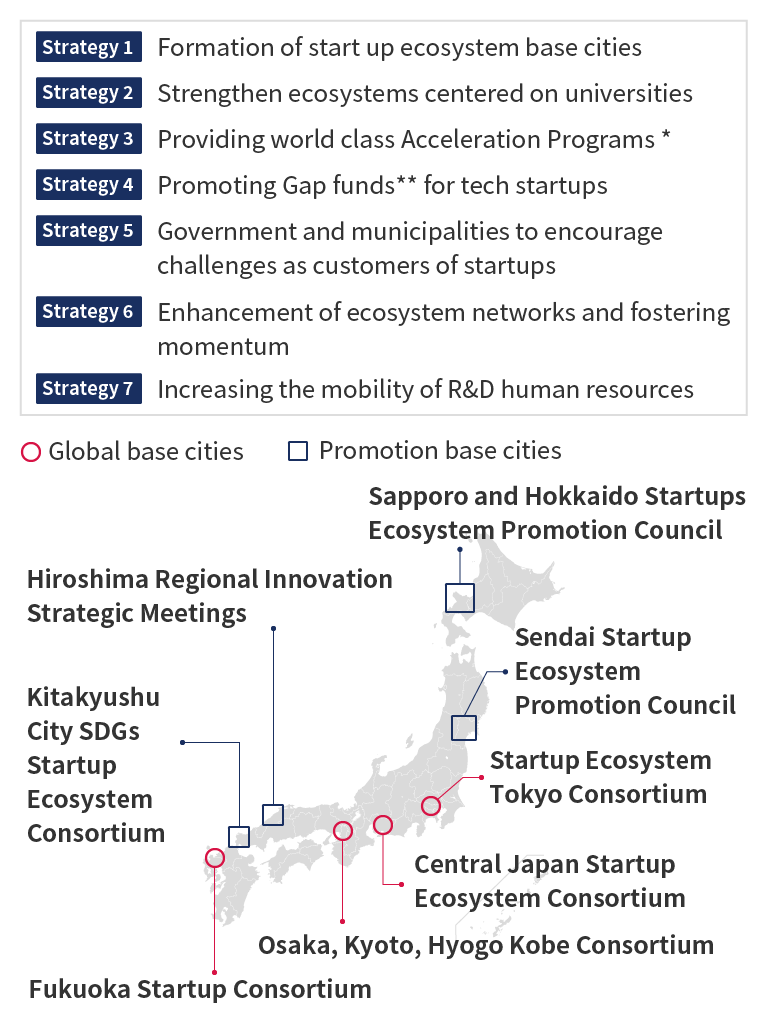
In July 2020, the Cabinet Office selected eight cities - four global startup cities and four startup cities (Chart 2-5), to build innovation cities open to the world. The eight cities involve 18 local governments, which provide intensive support for startups located in these municipalities over a three-year period.
Source: JETRO website
The "Support Package for the Formation of a Startup Ecosystem" formulated by the Cabinet Office, the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, includes the promotion of entrepreneurship education to learn about the mindset needed to start a business, the formation of networks and communities for education and support, the development of R&D systems for the creation of startups, and the generation of promising university startups with high growth potential. In addition, as part of the package, nine government agencies that support startups have concluded MOUs to strengthen their support systems.
JETRO will focus on supporting startups in regions to further promote the revitalization of the regional ecosystems. In February 2021, JETRO implemented an acceleration program by a U.S. accelerator for 49 startups in four global startup cities on strategy planning and measures to acquire human resources. To provide full-scale support, JETRO plans to expand the program by including the four startup cities on top of the four global startup cities from the fall of 2021 and offer online acceleration programs, including specialized courses, to about 100 startups. JETRO will implement the program from late October 2021 to February 2022.
Promoting the Super City Initiative
The Super City Initiative is an effort to improve the lives of citizens by providing advanced and convenient services through the use of cutting-edge technologies such as AI and big data in a wide range of fields spanning all aspects of life, including travel, logistics, education, and medical care. In May 2020, a law was enacted to partially revise the National Strategic Special Zones Law, setting forth the institutional framework for the Super City Initiative, and the revised law came into effect in September of the same year.
In December 2020, the Cabinet Office launched a public invitation for proposals on areas to be designated as special zones, advanced services to be implemented, and regulatory reforms in order to set up a super-city-type National Strategic Special Zones. A total of 31 municipalities applied by the time it closed on April 16, 2021. In August, an exclusive meeting was held to discuss zoning was held and based on the opinions of the members of the meeting, a call for resubmission of regulatory reforms was made by October 15, the same year. Regarding re-proposals, 28 of the 31 municipalities made proposals. The technical Committee will meet again in the future when there are more concrete proposals for regulatory reform. Thereafter, the National Strategic Special Zones Advisory Council will hold a meeting to express opinions on the proposed zone designations, followed by a Cabinet Order to designate the zones.
Revision of Tax Deduction System for Research and Development (R&D Tax Credit System)
METI has reviewed the R&D tax system in the fiscal 2021 tax reform in order to encourage companies that actively maintain or expand R&D investment. The tax system allows companies conducting R&D to deduct a certain percentage (2-14%) of their R&D expenditures from the amount of corporation tax. As a result of the tax reform in fiscal 2021, the following four points are implemented: 1) raise of the maximum deduction from the current maximum of 45% to a maximum of 50% of corporation tax; 2) revise of the tax credit rate to maintain and increase R&D expenditures; 3) addition of R&D related to software that provides services through the cloud to the scope of this tax credit, assuming automatic infrastructure inspection services using drones, etc., and mobility services such as sharing; and 4) open innovation-type operational improvements.
JETRO Invest Japan Report 2021
-
Chapter1.
Macroeconomic and Inward/Outward Foreign Direct Investment Trends in the World and Japan
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
-
Chapter2.
Japan's Business Environment and Foreign-Affiliated Companies
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
Section3.
-
-
Chapter3.
JETRO's Efforts to Promote Investment in Japan
-
Section1.
-
Section2.
-
お問い合わせ
フォームでのお問い合わせ
ジェトロはみなさまの日本進出・日本国内での事業拡大を全力でサポートします。以下のフォームからお気軽にお問い合わせください。
お問い合わせフォームお電話でのお問い合わせ
-
- 拠点設立・事業拡大のご相談:
- 03-3582-4684
-
- 自治体向けサポート:
- 03-3582-5234
-
- その他の対日投資に関するお問い合わせ:
- 03-3582-5571
受付時間
平日9時00分~12時00分/13時00分~17時00分
(土日、祝祭日・年末年始を除く)